第一步:理解WordPress的模板加载机制
在动手修改之前,你必须明白WordPress是如何决定使用哪个文件来显示文章页的,这遵循一个清晰的层级顺序:
-
single-{post_type}.php:这是最精确的模板。single-post.php:用于显示所有“文章”(默认的文章类型)。single-product.php:如果你的网站使用了WooCommerce插件,这个文件会用于显示商品页面。single-{你的自定义文章类型}.php:用于显示你自定义的文章类型。
-
single.php:如果WordPress找不到上面那个更具体的模板,就会使用这个通用模板。 -
singular.php:这是所有“单一”页面(包括文章页和单独的页面,如“关于我们”)的备用模板。 -
index.php:这是WordPress的终极备用模板,如果以上所有模板都找不到,它会使用主页的模板来显示内容。 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)
要修改文章页,我们主要操作 single.php 文件,如果你的网站有自定义文章类型,并且希望它们有不同的样式,那么创建 single-{post_type}.php 会是更好的选择。
第二步:如何找到并编辑模板文件
你有几种方法可以访问和编辑这些文件,强烈推荐使用第一种方法。
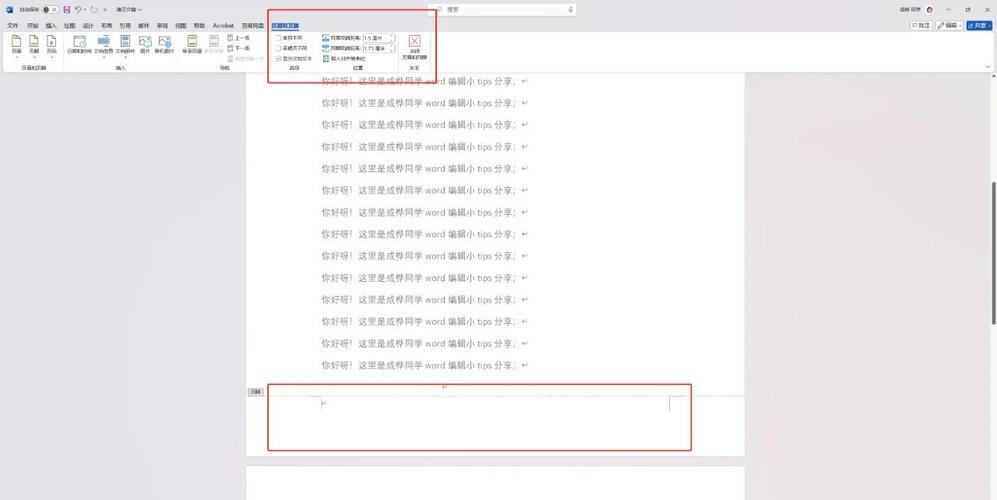
通过主题编辑器(最安全、最推荐)
这是最直接、最安全的方法,因为它直接在你的WordPress后台操作,无需使用FTP。
- 登录你的WordPress后台。
- 在左侧菜单中,找到 外观 -> 主题文件编辑器。
- 在右上角的下拉菜单中,选择你当前正在使用的主题。
- 在右侧的文件列表中,找到并点击
single.php。 - 现在你就可以看到并编辑文章页的模板代码了。
安全提示:在修改任何代码之前,强烈建议先备份你的主题,你可以通过在外观 -> 主题中“复制”当前主题来创建一个子主题,或者在修改前下载整个主题文件夹作为备份。
(图片来源网络,侵删)
通过FTP或文件管理器(更专业)
如果你使用的是代码编辑器(如 VS Code, Sublime Text),或者需要更复杂的操作,可以使用FTP或虚拟主机提供的文件管理器。
- 通过FTP工具(如 FileZilla)连接到你的服务器。
- 导航到WordPress的安装目录,然后找到
wp-content/themes/你的主题名称/。 - 在这里找到
single.php文件,将其下载到本地进行编辑。 - 编辑完成后,上传回服务器,覆盖原文件。
第三步:文章页模板的核心结构
一个典型的 single.php 文件结构如下,我会在关键部分加上注释:
<?php
/**
* Template Name: 文章页模板
* @package WordPress
*/
// get_header() 函数会加载主题的 header.php 文件
get_header();
?>
<div id="primary" class="content-area">
<main id="main" class="site-main" role="main">
<?php
// WordPress 主循环
// 如果有文章,则循环显示
if ( have_posts() ) :
// 加载循环前的模板部分,例如文章列表的标题等
// get_template_part( 'template-parts/content', 'header' ); // 可选
while ( have_posts() ) : the_post();
// --- 这是文章内容的核心部分 ---
// 加载一个名为 'content' 的模板部分
// 这是WordPress推荐的做法,让内容部分和结构部分分离
get_template_part( 'template-parts/content', get_post_format() );
// --------------------------------
// 文章导航(上一篇/下一篇)
the_post_navigation();
// 如果允许评论,加载评论模板
if ( comments_open() || get_comments_number() ) :
comments_template();
endif;
endwhile; // 结束 while 循环
else : // 如果没有文章
// 加载“未找到内容”的模板部分
get_template_part( 'template-parts/content', 'none' );
endif; // 结束 if ( have_posts() ) 循环
?>
</main><!-- #main -->
</div><!-- #primary -->
<?php
// get_sidebar() 函数会加载侧边栏
get_sidebar();
// get_footer() 函数会加载页脚
get_footer();
?>
关键点解释:
get_header()/get_footer():加载网站的头部和尾部。if ( have_posts() ) : ... while ( have_posts() ) : the_post(); ... endwhile; endif;:这是WordPress的“主循环”,负责从数据库中获取文章并逐个显示。get_template_part( 'template-parts/content', get_post_format() );:这是现代WordPress主题的最佳实践,它将文章的具体内容(标题、正文、元信息等)分离到了一个独立的文件中。- 这个文件通常位于
wp-content/themes/你的主题名称/template-parts/content.php。 - 如果你的文章是“图集”格式,WordPress会尝试寻找
content-gallery.php,这使得为不同格式(视频、音频、标准文章)定制内容变得非常容易。
- 这个文件通常位于
第四步:常见的修改示例
让我们来看看一些具体的修改场景。
示例1:在文章标题上方添加自定义文本
打开 single.php 文件,在 the_post(); 之后,get_template_part(...) 之前,添加以下代码:
<?php while ( have_posts() ) : the_post(); ?>
<h1 class="entry-title">
<?php _e( '正在阅读文章:', 'your-text-domain' ); ?> <?php the_title(); ?>
</h1>
<?php
// 原始的加载内容部分
get_template_part( 'template-parts/content', get_post_format() );
?>
<?php endwhile; ?>
示例2:在文章内容前后插入广告或自定义模块
同样在 single.php 中,修改 get_template_part 的调用。
<?php while ( have_posts() ) : the_post(); ?>
<?php
// 在文章内容前插入广告
if ( is_single() ) { // 确保只在文章页显示
echo '<div class="my-ad-before-content">广告代码</div>';
}
?>
<?php
// 加载文章内容
get_template_part( 'template-parts/content', get_post_format() );
?>
<?php
// 在文章内容后插入另一个模块
if ( is_single() ) {
get_template_part( 'template-parts/author-bio' ); // 假设你有一个作者简介模块
}
?>
<?php endwhile; ?>
示例3:修改文章元信息(作者、日期、分类等)
文章的元信息(如“发布于2025年10月27日,作者张三”)通常位于 content.php 文件中,而不是 single.php。
- 通过主题编辑器,打开
template-parts/content.php。 - 找到类似
<?php twentytwenty_posted_on(); ?>或直接包含the_author(),the_date()的代码块。 - 根据你的需求修改或删除它们。
如果你想添加自定义元信息,阅读时间”,可以在 content.php 中添加如下函数:
// 在 functions.php 中添加一个计算阅读时间的函数
function reading_time() {
$content = get_post_field( 'post_content', $post->ID );
$word_count = str_word_count( strip_tags( $content ) );
$reading_time = ceil( $word_count / 200 ); // 假设每分钟阅读200字
if ( $reading_time <= 1 ) {
$output = '1 分钟阅读';
} else {
$output = $reading_time . ' 分钟阅读';
}
return $output;
}
// 在 content.php 中调用这个函数
echo '<span class="reading-time">' . reading_time() . '</span>';
第五步:最佳实践与进阶技巧
-
使用子主题:这是最重要的建议! 直接修改父主题的文件,在父主题更新后,你的所有修改都会丢失,创建一个子主题,所有的修改都在子主题中进行,这样既安全又方便。
- 子主题只需包含你修改过的文件(如
single.php,functions.php)和style.css(用于声明父主题)。
- 子主题只需包含你修改过的文件(如
-
优先使用
get_template_part()、头部、底部等拆分成独立的模板部分,让代码结构更清晰,易于维护。 -
利用钩子:对于一些小修改,比如在文章前后添加内容,不要直接修改模板文件,使用WordPress的钩子,
the_content,在functions.php中添加,这样更灵活。// 在 functions.php 中添加 function add_content_before_post( $content ) { if ( is_single() && ! is_admin() ) { $custom_content = '<div class="before-post-notice">提示:本文最后更新于 ' . get_the_modified_date() . '</div>'; $content = $custom_content . $content; } return $content; } add_filter( 'the_content', 'add_content_before_post' ); -
使用页面构建器:如果你使用的是 Elementor, Beaver Builder 或 Gutenberg(古腾堡编辑器)等页面构建器,你可能根本不需要去碰
single.php文件,你可以在主题设置或构建器中直接设计文章页的布局,这通常更直观、更安全。
| 修改目标 | 推荐方法 | 文件位置 |
|---|---|---|
| 简单布局调整 | 直接编辑 single.php |
wp-content/themes/你的主题/single.php |
| 修改文章内容样式 | 编辑 content.php |
wp-content/themes/你的主题/template-parts/content.php |
| 添加功能性代码 | 在子主题的 functions.php 中使用钩子 |
wp-content/themes/子主题/functions.php |
| 完全自定义布局 | 创建子主题的 single.php 或使用页面构建器 |
wp-content/themes/子主题/single.php |
遵循这些步骤和原则,你就能安全、高效地修改WordPress文章页模板,让你的网站与众不同。